Stem cells from different sources to treat premature ovarian failure
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Stem cells from different sources to treat premature ovarian failure
Stem cells from different sources to treat premature ovarian failure. Research progress on the mechanism of stem cells from different sources in the treatment of premature ovarian failure.
The research progress on the effects and mechanisms of MSCs from different sources in the treatment of POF is summarized as follows.
Premature ovarian failure (POF) is a common endocrine disease in gynecology. At present, it is believed that the onset of POF is related to chemotherapeutic drug damage, autoimmune function, genetics, and metabolic abnormalities.
Although hormone replacement therapy can change some clinical symptoms, it cannot effectively restore ovarian function and fertility, and it may also cause obvious adverse reactions.
In recent years, a large number of studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) from various tissues and the cytokines and exosomes secreted by them mainly restore POF by improving the microenvironment of ovarian tissue, immune regulation, promoting follicular development or differentiation into granular cells. The ovarian function and fertility of the patient.
The research progress on the effects and mechanisms of MSCs from different sources in the treatment of POF is summarized as follows.
The feasibility of MSC for PoF
Studies have shown that MSC can play an immunomodulatory effect by up-regulating Treg cells, increasing the secretion of anti-inflammatory factors, and down-regulating the level of inflammatory factors. Under certain conditions, MSC can be directed to induce differentiation into three different germ layers, such as osteoblasts, chondroblasts, adipocytes, nerve cells, and hepatocytes.
Therefore, MSC is used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, diabetes, liver cirrhosis, pulmonary fibrosis and myocardial infarction, degenerative diseases (spinal cord injury, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease) and so on.
However, many common characteristics of MSC make it an ideal candidate for clinical treatment of POF.

The effect and mechanism of bone marrow MSC in the treatment of POF
In recent years, many studies have reported the good effect of bone marrow MSC in the treatment of POF. Bone marrow MSCs were injected intraperitoneally into cyclophosphamide-induced POF rats at 4×10^6 cells/kg, or injected into cisplatin-induced POF rats through the tail vein. Bone marrow MSCs can quickly migrate and home To the damaged ovary, it protects the gonadal toxicity caused by chemotherapy by reducing DNA damage and reducing follicle apoptosis, and accelerates the repair of ovarian tissue.
The mechanism of action of bone marrow MSC involves the miR-2l/PTEN/P13K/Akt signaling pathway.
The role and mechanism of amniotic fluid stem cells (AFSC) in the treatment of POF
AFSC was transplanted into chemotherapy-induced POF mice. The results of immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry showed that human specific nuclear antigen and follicle stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR) were mainly expressed around oocytes, indicating that AFSC differentiated into granular cells .
After AFSC transplantation, the expression of AMH in the ovarian tissue of POF mice is up-regulated. The latter can inhibit FSH, inhibit excessive follicle recruitment, and control the formation of primordial follicles, indicating that AFSC can directly differentiate into granulosa cells to promote follicle formation, or it can be up-regulated The expression of AMH indirectly restores the ovarian reserve function of POF mice.
Amniotic fluid stem cells are rich in miR through their exosomes. 146a and miR. 10a down-regulates the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins; amniotic membrane MSCs highly express Nanog, which can initiate JAK/STAT signal and increase the levels of HGF and other cell growth factors or anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2.
The effect and mechanism of amniotic membrane MSC (AMSC) in the treatment of POF
AMSC can secrete a large amount of collagens of type I, II, III, IV, VI. These collagens can make AMSC survive longer in POF mice and improve the therapeutic effect of AMSC. AMSC also highly expresses the transcription factors OCT4 and Nanog, the latter increases growth factors such as osteoprotegerin, HGF, BDNF, TGF-B2, EGF and FGF-7, and chemokines such as MCP-3, MCP- 2. The expression of MIP-3, GCP-2, ENA-78 and LIF promotes the proliferation of granulosa cells and restores damaged ovarian function4.
Amniotic membrane MSCs highly express Nanog, which can initiate JAK/STAT signal and increase the levels of HGF and other cell growth factors or anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2.
The effect and mechanism of placental-derived MSC (PMSC) in the treatment of POF
Studies have reported that PMSC transplantation can significantly improve the serum levels of high gonadotropins and low estrogen in POF mice induced by zona pellucida glycoprotein 3 (ZP3), promote follicular development, inhibit excessive follicular atresia and granulosa cell apoptosis, and improve ovaries Reserve capacity.
The mechanism of PMSC may involve the secretion of various cytokines by PMSC to reduce the apoptosis of granulosa cells in preantral follicles and cystic follicles, while various cytokines secreted by granulosa cells increase the expression of AMH through the TGF-p/Smad signaling pathway. The latter inhibits primordial follicle recruitment and follicular development, avoids premature exhaustion of the primordial follicle pool, improves ovarian reserve, and restores POF ovarian function.
The effect and mechanism of umbilical cord MSC (UCMSC) in the treatment of POF
Intravenous injection of uCMSC into cyclophosphamide-induced POF mice can significantly reduce granulosa cell apoptosis, increase the number of follicles, increase estrogen levels, and effectively restore ovarian function.
The mechanism of action of umbilical cord MSC is mainly paracrine multiple cytokines and exosomes, up-regulate the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, down-regulate the expression of pro-apoptotic protein, and increase the expression of DNA repair enzyme PARP.
The effect and mechanism of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC) in the treatment of POF
Studies have found that ADSC transplantation treatment of cyclophosphamide-induced POF mice can significantly up-regulate the expression of Angptl, Zcchcll and Oneeut2 genes, and down-regulate the expression of CXCR4 to promote the development of primordial follicles into mature follicles, but no direct differentiation of ADSCs into follicular cells was seen.
ADSC can also secrete HGF, VEGF, TGF. Cytokines such as B and PGF reduce granular cell apoptosis, increase the number of follicles, and restore ovarian function.
The main mechanism of action: VEGF and TGF are para-secreted by fat MSC. Bl, FG mounds and HGF, etc.; menstrual blood MSCs are mainly differentiated into ovarian granule-like cells to improve the ovarian microenvironment, so as to reduce granular cell apoptosis and follicular atresia, and promote granular cell proliferation and follicular development.
Clinical case
The results of a stem cell treatment of premature ovarian failure in young women proved the miraculous effect of stem cells.
In this study, mesenchymal stem cells were extracted from the iliac crest of patients who have received treatment, and the cells were implanted into the patient’s own ovary through minimally invasive laparoscopic methods, while ensuring that the other ovary was not affected.
After that, the researchers conducted regular investigations on the patient’s blood routine, ovarian imaging, and menopausal symptoms.
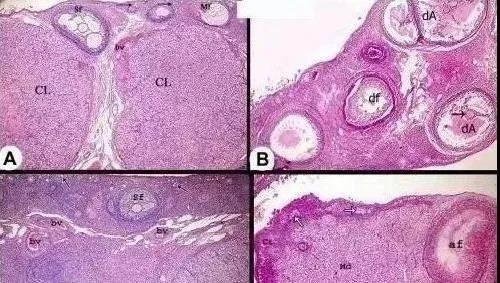
△ After stem cell treatment, the ovarian volume and the number of follicles at various levels increased significantly
The results showed that the ovary on the treated side was significantly larger than the ovary on the control side, and the patient had no obvious side effects after receiving the stem cell treatment.
What is even more surprising is that the serum estrogen levels of 5 of the participants who have completed the treatment began to increase 3 months after the injection of stem cells, and the effect was maintained for at least one year! And their menopausal symptoms were completely eliminated. In addition, the menstrual cycle of 7 participants also returned to normal.
Summary:
MSCs from different sources have similar curative effects in the treatment of POF, and may exert therapeutic effects through similar or different mechanisms. These all indicate that MSC has an attractive clinical transformation application prospect in the treatment of POF, especially in restoring the reproductive function of POF patients. , Even in the aspect of female aging that is complicated by POF, there is a huge market demand.
Therefore, in view of the known causes or mechanisms of POF, comprehensive and in-depth evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of MSC transplantation treatment, especially the evaluation of the long-term impact of parents and offspring, is still a key issue that needs to be resolved.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



