A multi-organ differential transcriptional map of early SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus monkeys
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
A multi-organ differential transcriptional map of early SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus monkeys
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
A multi-organ differential transcriptional map of early SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus monkeys.
SARS-CoV-2, one of the human respiratory coronaviruses, is highly transmissible, and its infection triggers the body’s innate immune response, leading to pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
However, more and more COVID-19 patients show liver, heart, kidney, vascular system, and even nervous system damage and severe rehabilitation sequelae.
The whole transcriptome of each organ in the body after SARS-CoV-2 infection was systematically studied.
Changes are necessary to understand the mechanisms of the host immune response.
On April 4, 2022, the team of Yang Yungui, Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences ( National Center for Bioinformatics) , Tong Weimin ‘s team of the Institute of Basic Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Qin Chuan ‘s team of the Institute of Medical Laboratory Animals, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences jointly published in Protein & Cell online.
The results of the study titled Differential transcriptomic landscapes of multiple organs from SARS-CoV-2 early infected rhesus macaques.
By performing RNAscope, digital PCR, immunohistochemical staining and transcriptome sequencing (RNA-Seq) on multiple organs of rhesus monkeys in the early stage of SARS-CoV-2 infection , the research team found that SARS-CoV-2 is widespread in various tissues and organs.
The distribution and replication of cerebral cortex; the differential transcriptional changes in various tissues and organs were drawn; the specific expression of NRP1 receptors in cerebral cortex tissue and the close signaling between tissues, as well as enhanced inflammation and innate immune responses may lead to Potential mechanisms of viral encephalitis .

The research team first collected and extracted multiple organs and tissues from healthy control rhesus monkeys (1 male) and rhesus monkeys 7 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection (2 males, 1 female) , including lung, cerebral cortex, Brain stem, cerebellum, medulla, left ventricle, right ventricle, muscle, kidney, spleen, liver, intestine, stomach, and reproductive organs (testis/ovary) , RNAscope and digital PCR experiments were performed, and SARS-CoV-2 was found in Extensive replication and transcriptional signals exist in various tissues and organs .
Through transcriptome sequencing of each tissue and organ, the differential transcriptional change map of each tissue and organ was drawn, and it was found that the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and right ventricle tissue showed strong transcriptional changes in the early stage of SARS-CoV-2 infection .
Transcriptional changes in the cerebellum and right ventricle tissues were similar and opposite to those in the cerebral cortex, and there was a close signal exchange between the tissues. Interferon receptors and SARS-CoV-2 receptor NPR1 are specifically elevated in the cerebral cortex after infection with SARS-CoV-2, exhibiting enhanced pro-inflammatory and innate immune responses .
Elevated mRNA and protein levels of inflammatory cytokines released by macrophages and enhanced interstitial infiltration of CD3 + T lymphocytes and CD68 + macrophages suggest that macrophages secrete M1-related inflammatory cytokines, leading to increased inflammatory cytokines in neurons.
Activated inflammatory response leading to viral encephalitis caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection .
In summary, this study, combined with the systematic analysis of biological experiments and transcriptome sequencing data, found the widespread distribution of SARS-CoV-2 infection in many tissues and organs of the body, and drew a detailed transcriptome map. Characterization of inflammatory and innate immune responses to unravel the underlying mechanism of viral encephalitis induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection.
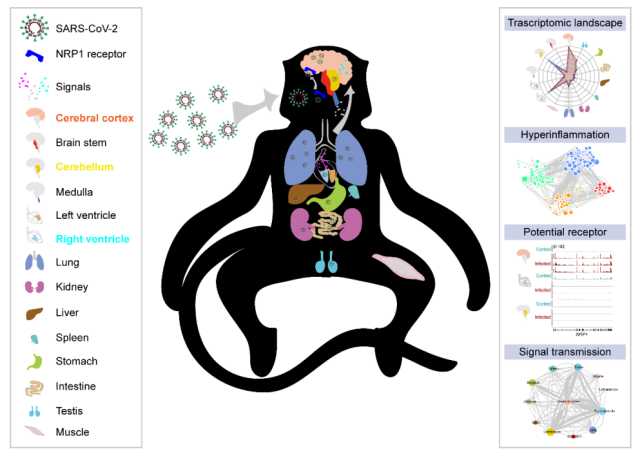
A multi-organ differential transcriptional profile of rhesus monkeys during early SARS-CoV-2 infection
Researcher Yang Yungui and Associate Researcher Yang Ying of Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (National Center for Bioinformatics) , Professor Tong Weimin of Institute of Basic Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and Professor Qin Chuan of Institute of Medical Laboratory Animals, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences are the co-corresponding authors of this article.
Dr. Gao Chunchun, special research assistant of Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (National Center for Bioinformatics) , Li Man, deputy chief technician of the Department of Pathology, Beijing Ditan Hospital, and Deng Wei, associate researcher of Institute of Medical Laboratory Animals, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences are the co-first authors of this article.
Reference:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13238-022-00915-5
A multi-organ differential transcriptional map of early SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus monkeys
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



