The world first broad-spectrum antiviral drug opens Phase 2 clinical trials
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
The world first broad-spectrum antiviral drug opens Phase 2 clinical trials
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
The world first broad-spectrum antiviral drug opens Phase 2 clinical trials: Against all viruses acting through autophagy.
Recently, the Korean pharmaceutical company Hyundai Bioscience announced the launch of the phase II clinical trial of CP-COV03.
Unlike traditional antiviral drugs targeting specific viruses, this antiviral drug developed by South Korea has an innovative mechanism of “removing the virus” and can be applied to all The virus , if its effectiveness can be confirmed through clinical trials, will hopefully write a new chapter in the history of antiviral drugs in the world.
Hyundai Bioscience said that CP-COV03 is a broad-spectrum viral therapy drug that can be applied to various viruses, including the new coronavirus . The company has recruited patients diagnosed with the new coronavirus who participated in the drug delivery trial and entered the phase II clinical trial of the antiviral oral drug candidate CP-COV03.

CP-COV03 is an innovative broad-spectrum antiviral drug. Its pharmacological effect is that when the virus invades the cell, the cell can recognize the foreign body and initiate ” autophagy ” on its own to remove all the virus.
If the effective performance of CP-COV03 against the new coronavirus is confirmed in this clinical trial, the world’s first product that can be applied to the new coronavirus and its variants, influenza, hepatitis, AIDS, Ebola, herpes will be born All the broad-spectrum antiviral drugs that plague human viruses have attracted the attention of the scientific community.
From this point of view, the clinical results of the new coronavirus of CP-COV03 are expected to be the “trumpet call” announcing the birth of broad-spectrum antiviral agents.
Existing antiviral drugs are mainly suitable for inhibiting specific viral replication mechanisms. The toxicity of the drugs brings certain limitations to patients taking the drugs, and problems such as viral drug resistance may also occur when they are taken for a long time.
In contrast, the efficacy of CP-COV03 is cell-targeted , has the characteristics of a new concept antiviral drug, and gets rid of various shortcomings of existing antiviral drugs.
This clinical trial of CP-COV03 aims to launch ” the world’s first broad-spectrum antiviral drug “, which in many respects is very similar to the human efficacy trial of penicillin conducted in 1941, which has attracted great attention from the scientific community.
Penicillin is the world’s first broad-spectrum antibiotic. Its pharmacological mechanism is that when a bacterial infection occurs, Penicillium will produce an antibiotic in order to survive, inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, and ultimately kill bacteria. The birth of penicillin freed mankind from the fear of bacteria.
Hyundai Bioscience said confidently: ” After discovering the mechanism of killing bacteria, human beings found a substance that exerts the relevant mechanism of action, and thus the life-saving drug of the 20th century – penicillin was born. CP-COV03 has the mechanism of autophagy to clear viruses, Like penicillin, it will be the first broad-spectrum drug in the field of viruses. ”
If CP-COV03 can become the first broad-spectrum antiviral drug, after patients are infected with the virus in the future, they can be prescribed a broad-spectrum treatment drug, quickly take active response measures, and even cut off the global pandemic of the virus.
In this way, the current virus response route, which is the first to rely on vaccines, will also undergo dramatic changes when dealing with a collective infection of the virus.
The 20th century life-saving drug that allows humans to defeat bacteria – penicillin
The development of the broad-spectrum antibiotic ” penicillin ” is considered one of the top ten events in the medical field of the twentieth century.
In 1928, British bacteriologist Alexander Fleming accidentally discovered penicillin in Penicillium, and then he started the research and development of antibacterial agents, but it ended in failure.
Since then, two scientists from Oxford University, Howard Flory and Ernst Chain, developed the world’s first antibiotic in 1942 through follow-up research.
In the First World War, bacterial pneumonia infection caused a mortality rate as high as 18%, but in the Second World War, penicillin significantly reduced the mortality rate to less than 1%.
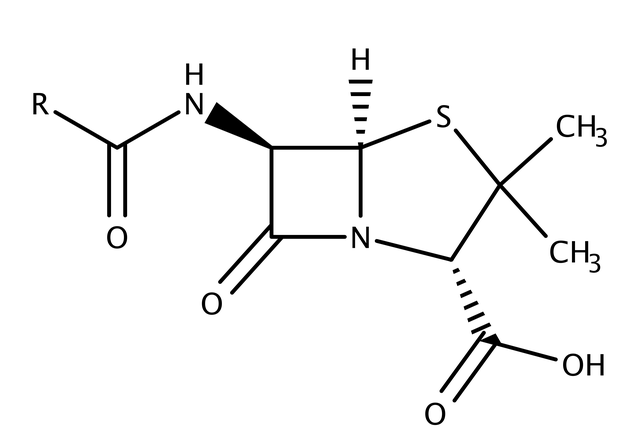
Penicillin is an antibiotic produced by the microorganism “Penicillium” in order to survive when it is attacked by bacteria.
It can inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls and ultimately play a role in sterilization.
At that time, people elucidated the mechanism of killing bacteria, and found substances that can exert this mechanism.
Thus, penicillin, a life-saving drug in the 20th century, was born. In addition to staphylococcus, penicillin has antibacterial effect on streptococcus, meningitis, gonorrhea, diphtheria and other broad-spectrum bacterial infections, so that humans can get rid of the fear of bacteria.
Humans have defeated bacteria with this potent broad-spectrum antibiotic, but have so far failed to develop a broad-spectrum treatment as reliable as penicillin in the field of major viral infections.
Because humans have not yet found a mechanism that can eliminate various types of viruses like penicillin can eliminate various bacteria, and have not found a substance with this pharmacological effect.
Cells that kill viruses ‘autophagy’
Human cells have the characteristics of degrading and recycling unnecessary internal proteins, which is the ” autophagy ” function of cells .
Cells protect themselves from bacterial or viral attacks through this autophagy, which can be said to be an immune effect.
Research on autophagy began in the mid-1950s. At that time, scientists discovered that there are organelles that decompose substances in cells – lysosomes .
Its discoverer, Christian de Duve , used ” autophagy ” once to describe the process of cells actively decomposing substances through lysosomes.
Japanese scientist Yoshinori Ohsumi won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 2016 for discovering genes that play an important role in the autophagy process.
When the virus containing the protein invades the host cell, it will inhibit the cell from autophagy to prevent it from being broken down by autophagy.
However, through various studies and experiments, the scientific community finally found that niclosamide has the pharmacological effect of promoting autophagy.
The main ingredient of CP-COV03 is “niclosamide”
The main component of CP-COV03, niclosamide, is a drug developed by Bayer in Germany in 1958.
Due to the low bioavailability of the drug (the ratio of the injected dose to the bioabsorbed drug) , it has been used as a parasitic drug for many years.
Since 2000, studies by multiple institutes have found that the drug is effective against various viruses such as SARS, hepatitis C, herpes and influenza, Ebola, Zika, AIDS, MERS, and novel coronavirus.
The efficacy of niclosamide in humans has been demonstrated in the clinical trials of this study, but the need to improve bioavailability remains a challenge.
Hyundai Bioscience said it has increased the bioavailability of niclosamide by a factor of 40 through its proprietary drug delivery technology and is therefore confident of passing Phase II clinical trials.
The world first broad-spectrum antiviral drug opens Phase 2 clinical trials
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



