Regular milk consumption is associated with prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
Regular milk consumption is associated with prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
New research shows that regular milk consumption is associated with increased risk of prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women.
On June 8, 2022, researchers from Loma Linda University published a research paper titled: Dairy foods, calcium intakes, and risk of incident prostate cancer in Adventist Health Study–2 in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition .
The study showed that men with a higher intake of dairy products (primarily milk) had a significantly increased risk of prostate cancer compared with men with a lower intake of dairy products (primarily milk).
Furthermore, this risk was not associated with non-dairy calcium intake, suggesting that components other than calcium in dairy products play a role in prostate cancer risk.

Our findings add an important weight to other evidence that identifies dairy, but not non-dairy calcium, as a modifiable risk factor for prostate cancer.
Gary Fraser, the study’s lead investigator and a professor at Loma Linda University’s School of Medicine and Public Health, said.
The research team tracked the dietary intake of more than 28,000 men in North America who were cancer-free at the start of the study. Dietary intake was estimated by food frequency questionnaires and 24-hour recall.
Baseline questionnaires included demographics, family history of prostate cancer, physical activity, alcohol consumption, prostate cancer screening, and body mass index (BMI) .
The research team then used the Cancer Status Registry to track the prostate cancer status of the follow-up participants for an average of nearly eight years.
By the end of the study period, 1,254 of these participants had prostate cancer.
The results of the analysis showed that men who consumed about 430 grams of dairy products per day (among all participants) consumed about 430 grams of dairy per day, compared to men who consumed only 20.2 grams per day ( in the lowest 10% of all participants). intake in the top 10% ) increased the risk of prostate cancer by 27% .
Additionally, men who consumed about 430 grams of dairy per day had a 62% increased risk of prostate cancer compared to men with zero dietary dairy intake .
The team noted that there was little difference in the results between whole milk, reduced-fat or skim milk.
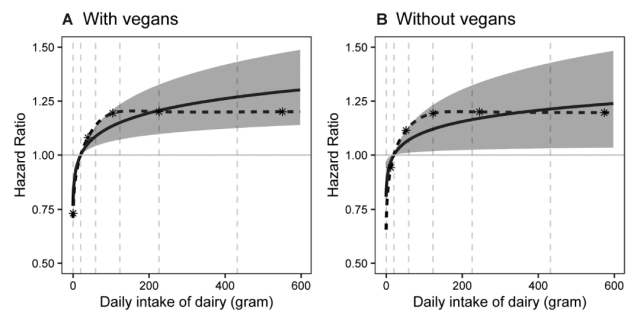
A possible reason for these associations between prostate cancer and cow’s milk is the sex hormone content in cow’s milk, the team said .
Up to 75% of lactating cows are pregnant, and prostate cancer is a hormone-responsive cancer.
Previous research has shown that consumption of dairy and other animal proteins is associated with higher blood hormone levels, and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) is thought to promote certain cancers, including prostate cancer.
In addition, a paper published by the team last year showed that dairy intake was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in women .
The research team believes that the association of dairy products with male prostate cancer and female breast cancer may be the same biological mechanism.
It is worth mentioning that on May 6, 2022, researchers from the University of Oxford , the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking University jointly published a paper entitled: Dairy consumption and risks of total and site-specific cancers in Chinese in the journal BMC Medicine adults: Research paper for an 11-year prospective study of 0.5 million people .
The study, which followed more than 510,000 Chinese for an average of up to 11 years, found that among Chinese adults, higher dairy intake was associated with a higher risk of liver cancer and breast cancer in women.

Using data collected from 510,146 Chinese adults from the China Kadoorie Biobank Prospective Study, the research team analyzed the relationship between dairy intake and cancer risk .
The study recruited volunteers aged 30-79 years from 2004-2008 from 10 different regions (5 urban and 5 rural) across the country.
The 10 regions were chosen to cover a broad range of risk factors and disease patterns, with 97% of participants being Han Chinese, 59% female, and 44% living in rural areas.
Trained medical professionals collected information on the frequency of consumption of major food groups, including dairy, as well as their sociodemographic characteristics, disease history, and lifestyle, from participants through questionnaires at specially established local sites.
Among the more than 510,000 people included in this study, 20.4% regularly consume dairy products (at least once a week) , 68.5% never or rarely consume dairy products, and the average dairy consumption of the population is 37.9 grams, while the average consumption of regular eaters was 80.8 grams per day.
During a mean follow-up period of 10.8 years, a total of 29,277 cancer cases between the ages of 35 and 79 were recorded. The data included age, region, education level, household income, smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, family history of cancer, body mass index (BMI) , soy and fresh fruit intake, and chronic hepatitis B virus infection (for liver cancer) . After adjusting for a series of factors that could lead to confounding effects, the researchers found that dairy intake was significantly and positively associated with cancer risk :
- Regular consumption of dairy products increased the overall risk of cancer by 9%, the risk of liver cancer by 18%, and the risk of breast cancer in women by 22%.
- For every 50 grams of dairy products consumed per day, the risk of overall cancer, liver cancer and breast cancer in women increased by 7%, 12% and 17%, respectively.
- Regular consumption of dairy products had a 23% increased risk of lymphoma , but this association lost statistical significance after adjustment for multiple testing.
- The study did not find a significant association between dairy intake and the risk of colorectal, prostate or other types of cancer.
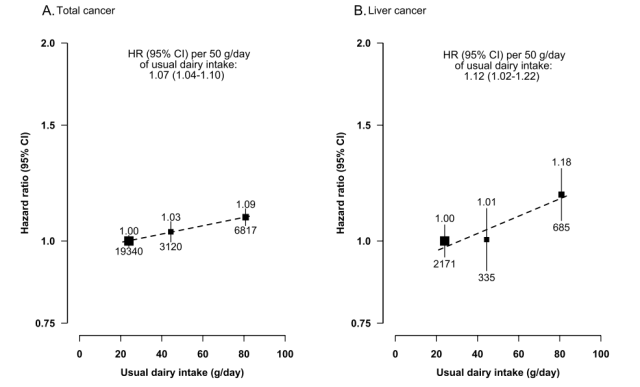
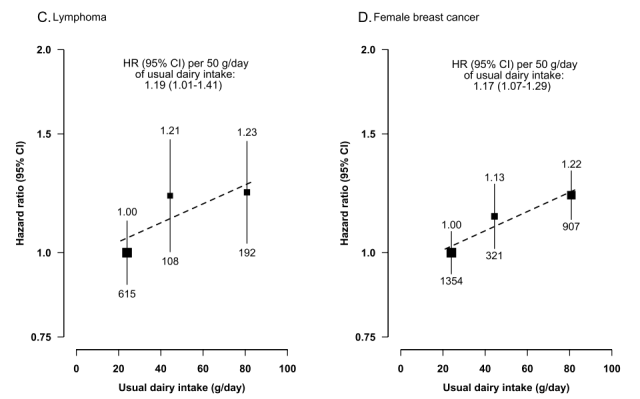
The authors also caution that the study has certain limitations, including that the number of cancer cases may not be large enough to allow reliable statistical analysis of some less common cancer types (such as lymphoma and prostate cancer) .
The study was an observational study rather than a randomized controlled trial, so the observed association cannot be used to establish a causal relationship between dairy intake and cancer risk. Further research is needed in the future to explore causality and the underlying underlying mechanisms.
The authors also said that while these findings suggest a possible direct link between regular consumption of dairy products and some cancers, it is important to be aware that dairy products contain proteins, vitamins and minerals that are important for health. It is not wise to limit dairy intake based solely on the results of current research.
Reference:
https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqac093
https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-022-02330-3
Regular milk consumption is associated with prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



