Gender Life Expectancy Gap Reaches New High
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Gender Life Expectancy Gap Reaches New High
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Gender Life Expectancy Gap Reaches New High
In mammals, females typically outlive males in life expectancy, and humans are no exception. According to statistics from the World Health Organization and the United Nations Population Division, women globally tend to have a longer average life expectancy than men.
A recent study indicates that the trend of women having a longer life expectancy than men has been widening over the past decade.
Researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health published a paper titled “Widening Gender Gap in Life Expectancy in the US, 2010-2021” in the JAMA Internal Medicine journal.
The study reveals that in 2010, the average life expectancy for women in the United States was 4.8 years longer than for men, and by 2021, this gap had increased to 5.8 years.

For over a century, women in the United States have consistently had a longer life expectancy than men, primarily due to lower risks of cardiovascular disease and lung cancer, often associated with smoking.
Between 2019 and 2021, the COVID-19 pandemic disproportionately affected men, leading to a significant loss in life expectancy. This period saw the largest increase in the gender life expectancy gap, followed by factors such as accidental injuries, drug overdoses, accidents, and suicides.
In recent years, numerous studies have explored the decline in human life expectancy, but few have systematically analyzed why the gap in life expectancy between men and women has been widening since 2010. In 2019, life expectancy in the United States was 78.8 years, dropping to 77.0 years in 2020 and further to 76.1 years in 2021.
Part of the reason for the decline in life expectancy among Americans is attributed to “deaths of despair,” a term referring to an increase in deaths due to reasons such as suicide, drug abuse, and alcoholic liver disease, often associated with economic hardships, depression, and stress.
The research team used data from the National Center for Health Statistics to identify the leading causes of reduced life expectancy. They then assessed the impact of these causes on men and women to understand how various factors contribute to the gender gap in life expectancy.
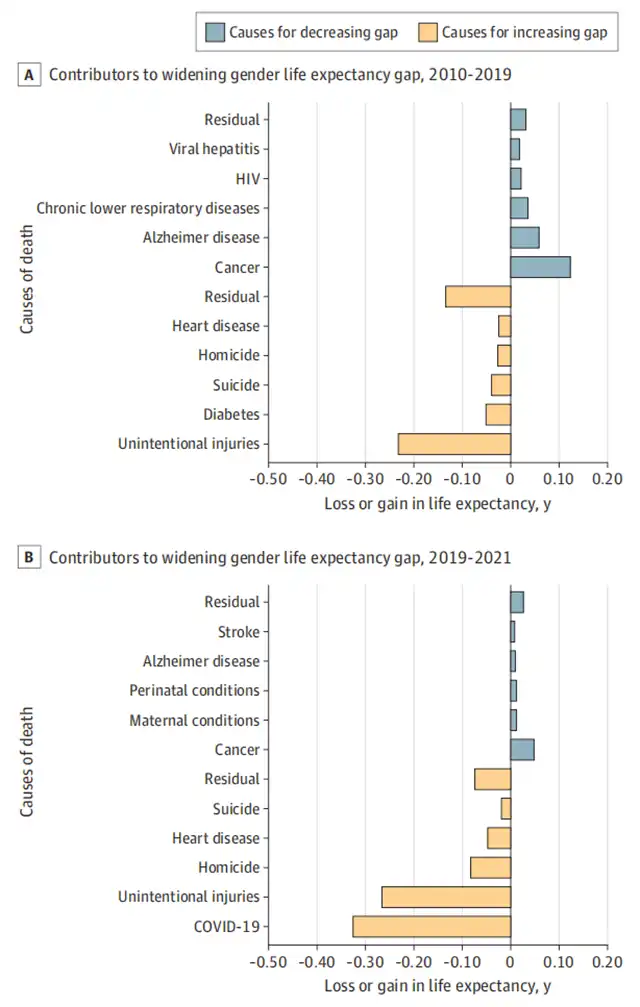
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the leading causes of reduced life expectancy were accidental injuries, diabetes, suicides, homicides, and heart disease. During the pandemic, men faced a higher risk of death from COVID-19 infection, possibly influenced by differences in health behaviors between genders and societal factors such as occupational risks, reluctance to seek medical care, incarceration, and homelessness. Chronic metabolic disorders and mental illnesses also played a role.
The research team suggests that these findings raise the question of whether more specialized care, particularly in mental health, should be provided to men to address the growing gap in life expectancy. As the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic diminishes, it remains essential to closely monitor trends in gender life expectancy.
Gender Life Expectancy Gap Reaches New High
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



