Summary of COVID-19 mutants and 80 Antigens
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
Summary of COVID-19 mutants and 80 Antigens
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Summary of COVID-19 mutants and 80 Antigens.
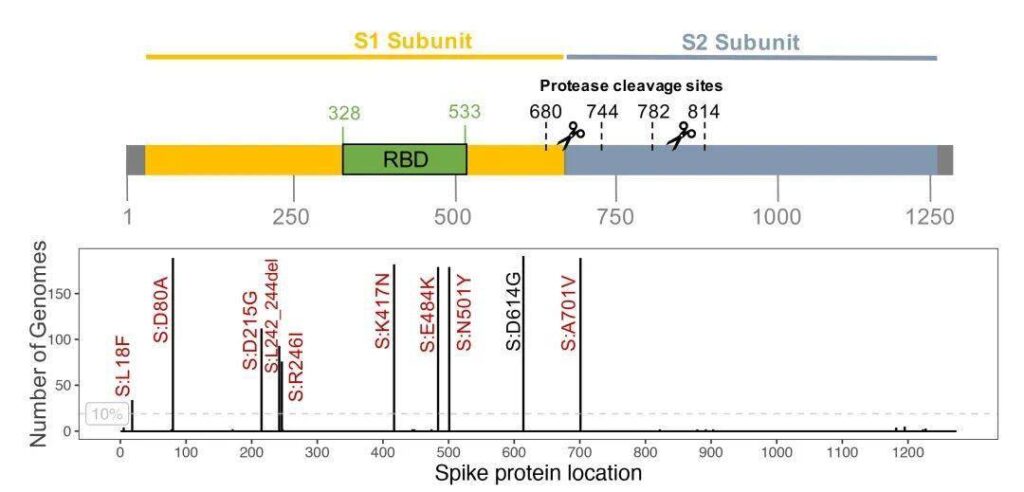
According to data from the National Center for Biological Information (CNCB), it is shown that there have been 3,225 mutations in the S protein of the new coronavirus, including 1,930 mutations that cause amino acid changes, and 253 amino acid mutations in the protein receptor binding domain (RBD) .
Recently, three new coronavirus mutant strains have attracted widespread attention around the world, namely the British B.1.1.7 mutant, the South African B.1.351 mutant and the Brazilian P.1 mutant.
Mutations in RBD may increase the affinity of binding to the receptor, weaken the effect of neutralizing antibodies, or cause viral immune escape. According to “Cell”, mutations at Q493, Q498 and N501 will increase the affinity of the virus with the ACE2 receptor on the surface of human cells and enhance the infectivity of the new coronavirus.
In mouse models, experiments have confirmed that N501Y can enhance the binding affinity of the virus to human and mouse ACE. The Furin protease cleavage site has a huge impact on the host cell binding ability, and the P681H mutation is close to the Furin cleavage site, which may be a factor that increases the affinity of S protein and ACE2 by a thousand times. 69-70del may help the virus escape the host immune response.
British B.1.1.7 mutant
The study found that this mutant strain has 23 special mutations, including 14 non-synonymous mutations (amino acid changes), 6 synonymous mutations (non-amino acid changes) and 3 deletions.
This is the first time it has been found in a strain There are so many variations. Among them, 8 mutations all occur in Spike protein.
The following 3 mutation sites are particularly concerned by researchers and need to be monitored.
– N501Y, can enhance the combination of new coronavirus and human or mouse ACE2
– 69-70del, can cause immune escape
– P681H, near the Furin restriction site
Yiqiao Shenzhou has successfully developed a variety of products related to this mutation site, which can be used in the research of neutralizing antibodies and vaccines for the new coronavirus:
| Study on important mutation sites of British mutant B.1.1.7 | ||
| Item No. | antigen | Mutation site |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40591-V08H7 | S1 | HV69-70 deletion, N501Y, D614G |
| 40591-V08H12 | S1 | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H |
| 40588-V07E7 (scheduled) | N | D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F |
| 40588-V07E8 (scheduled) | N | D3L, S235F |
| 40589-V08B6 (under development) | S-ECD | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H |
South Africa B.1.351 mutant
According to the research data of relevant units in South Africa, it was found that the mutant strain was mainly Spike protein with 8 mutations, including 3 important residues of RBD: K471N, E484K and N501Y. Among them, E484K and N501Y belong to receptor binding motifs, which are the main sites for binding to human ACE2 receptor.
South Africa mutant site (Source: medRxiv)
The study of mutants in South Africa found the most worrying thing. On January 19th, a US research team published a preprinted article in bioRxiv and found that the protective ability of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine against South African mutant strains may be reduced.
Researchers isolated neutralizing antibodies from vaccinated volunteers, of which 22 are The neutralizing activity of the antibody against a mutation site in the South African mutant decreased more than 5 times.
This reminds us that we need to strengthen the continuous monitoring of new coronavirus mutants.
Yiqiao Shenzhou also developed South African mutant related products for scientific research:
| Study on important mutation sites of South African mutant B.1.351 | ||
| Item No. | antigen | Mutation site |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40592-V08H84 | RBD | E484K |
| 40592-V08H59 | RBD | K417N |
| 40591-V08H10 | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G |
Brazil P.1 mutant
According to a report submitted by Faria et al. at Virological on the 13th, it was found that there were multiple mutations at K417T, E484K, and N501Y.

Phylogenetic tree of Brazil mutant strains and mutation sites (Source: Virological)
According to the published sequence information, Yiqiao Shenzhou recombinantly expresses the protein at the relevant mutation site in vitro, which can be used for research related to the new coronavirus:
| Study on important mutation sites of Brazilian mutant P.1 | ||
| Item No. | antigen | Mutation site |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40592-V08H84 | RBD | E484K |
Mink mutant
According to the SSI research report, 5 mutant strains were isolated from Danish mink, and Y453F has important research significance.
The amino acid at position 453 of the Spike protein of the Y453F mutant new coronavirus is mutated from tyrosine (Y) to phenylalanine (F), which may be to better adapt to the mink host. In addition to the Y453F mutation, it also includes: 69-70del, 692V, S1147L, M1229I, etc.
Yiqiao Shenzhou has developed two mink-related mutant recombinant proteins:
| Study on important mutation sites of mink mutants | ||
| Item No. | antigen | Mutation site |
| 40592-V08H80 | RBD | Y453F |
| 40591-V08H8 | S1 | ΔH69/ΔV70, Y453F, D614G |
At present, Yiqiao Shenzhou has developed more than 80 recombinant Spike and N antigen mutant proteins, covering a variety of mutation sites including the above-mentioned mutation sites.
The specific sites are as follows:
COVID-19 Spike Mutant Related Products List
SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Mutant
| P337S His tag | F338L His-Tag | V341IHis-Tag |
| F342LHis-Tag | A344SHis-Tag | A348SHis-Tag |
| N354DHis-Tag | A352SHis-Tag | S359N His tag |
| V367FmFc-Tag | V367FHis-Tag | N370SHis-Tag |
| A372SHis-Tag | A372THis-Tag | F377LHis-Tag |
| K378N His tag | K378R His tag | P384L His tag |
| T393PHis-Tag | V395IHis-Tag | T385AHis-Tag |
| D405V, Q414AHis-Tag | E406Q His-Tag | R408IHis-Tag |
| Q414EHis-Tag | Q409EHis-Tag | Q414R His-Tag |
| W436RHis-Tag | K417NHis-Tag | A435SHis-Tag |
| K444R His tag | N439K His tag | N440KHis-Tag |
| V445FHis-Tag | G446S His tag | G446VHis-Tag |
| L452R His tag | Y453FHis-Tag | L455FHis-Tag |
| F456L His tag | F456EHis-Tag | K458R His tag |
| K458QHis-Tag | E471Q His tag | I472VHis-Tag |
| G476SHis-Tag | S477R His tag | S477I His tag |
| S477NHis-Tag | T478I His tag | P479SHis-Tag |
| N481DHis-Tag | G482S His tag | V483AHis-Tag |
| V483IHis-Tag | E484KHis-Tag | E484QHis-Tag |
| N478RHis-Tag | G485SHis-Tag | F486S His tag |
| F490SHis-Tag | S494P His tag | F490LHis-Tag |
| P499R His tag | N501YHis-Tag | V503FHis-Tag |
| A520S His tag | Y505CHis-Tag | Y508HHis-Tag |
| A520VHis-Tag | P521RHis-Tag | P521SHis-Tag |
| A522VHis-Tag | A522S His tag | |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Mutant | ||
| N234Q His tag | D614GHis-Tag | D614G Fc Tag |
| HV69-70 deletion, Y453F, D614GHis-Tag | HV69-70 deletion, N501Y, D614GHis-Tag |
| K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614GHis-Tag | L18F, D614GHis-Tag |
| T20N, D614GHis-Tag | A222V, D614GHis-Tag |
HV69-70 deletion, Y144 deletion, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H
His-Tag
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1+S2 ECD Mutant |
R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P
His-Tag
Summary of COVID-19 mutants and 80 Antigens.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



