Four doses of inactivated vaccines are difficult to prevent COVID-19 variants
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
- Statins Lower Blood Lipids: How Long is a Course?
- Warning: Smartwatch Blood Sugar Measurement Deemed Dangerous
Four doses of inactivated vaccines are difficult to prevent COVID-19 variants
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Four doses of inactivated vaccines are difficult to prevent COVID-19 variants.
The research results of the fourth dose of the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine are released. How can the booster shot be effective?
Recently, the preprint platform MedRxiv released a study on the efficacy of the fourth dose of the COVID-19 vaccine from the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University.
The immune response elicited by the third dose of the inactivated vaccine was observed to decline significantly over time, and the purpose of this study was to investigate the post-vaccination situation with the four doses of the inactivated vaccine. The study selected 38 health care workers who voluntarily chose to receive the fourth dose 6 months after the third dose .
The study pointed out that after 6 months of vaccination, the protection of the third dose of the vaccine was greatly reduced. Comparing the geometric mean titers ( GMT ) of neutralizing antibodies in 382 weeks and 26 weeks after the third dose of inoculation , the protection against the original strain of the new coronavirus was reduced by 85% , and the protection rate against the new coronavirus variant strain Omicron was reduced by 53% .
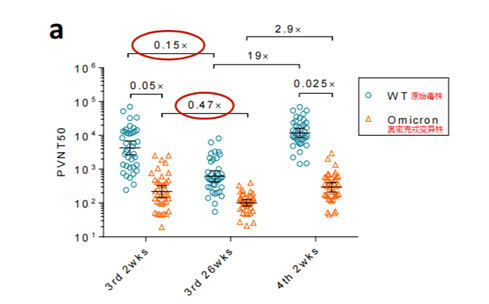
(As can be seen from the above figure, 6 months after inoculation of the third dose of inactivated vaccine, the level of neutralizing antibodies against the original strain decreased by 85% , and the level of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant decreased by 53% )
So, what are the conclusions and implications of this study for the effect of the fourth dose of inactivated vaccine?
Antibody levels after the fourth dose were lower than the same period of the third dose
As can be seen from Figure a below, the antibody level after the third dose of inactivated vaccine was significantly higher than that after the second dose, and the antibody level after the fourth dose was slightly lower than that after the third dose. The second dose dropped the rate, and the fourth dose raised antibody levels again, but did not reach the peak of the third dose.
As can be seen from Figure b below, the antibody level two weeks after the fourth dose was lower than the level two weeks after the third dose. In contrast , the antibody levels in dose 3 ( after 26 weeks ) were twice as high as those in dose 2 ( after 21 weeks) (panel c ).
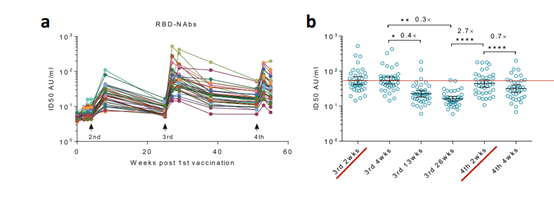
(As can be seen from Figure b , the antibody level two weeks after the fourth dose was lower than the antibody level two weeks after the third dose)
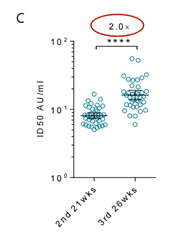
(As can be seen from Figure c , the antibody level after 26 weeks of the third dose was 2 times that after 21 weeks of the second dose)
Therefore, we can conclude that the immune response cannot be endlessly enhanced, and that there is a limit or even a “turning point” after repeated vaccinations. The above data show that the third dose is a “turning point” for repeated vaccination of the COVID-19 inactivated vaccine.
Four doses of inactivated vaccines are difficult to prevent COVID-19 variants
The study found that before and after the fourth dose of inactivated vaccine, the GMT (neutralizing antibody titer) of the original strain in the volunteers increased by 19 times, but the effect on Omicron was poor, only increased by 2.9 times. Previous studies at home and abroad have pointed out that the third dose of the COVID-19 vaccine evoked a higher immune response than the first two doses. However, the researchers compared the peak GMT after the third dose and the fourth dose , and found that the peak protection of the fourth dose against Omicron was similar to that of the third dose, and 2.8 times higher than the third dose for the original strain.
According to the study, to the researchers’ surprise, the GMT peaks after the third and fourth doses were negatively correlated, meaning that people who did better after the third dose received the fourth dose The effect is even worse.
As can be seen from the figure below, two weeks after the fourth dose of inoculation, the antibody level to Omicron was 0.025 times that of the original strain; and 26 weeks (half a year) after the third dose of inoculation , the antibody to Omicron was The level was 0.47 times higher than 2 weeks after inoculation .
Image
This study is similar to the trend of the previous results of the fourth dose of mRNA , which both show that the antibody activation reaches a bottleneck after repeated boosting of the same vaccine, especially for the Omicron variant, repeated boosting of the same vaccine is difficult to block infection.
In addition, this study also found that repeated inoculation of the inactivated vaccine shifted the humoral immune response from the S protein to the nucleocapsid, which is the key site for inducing the immune response. From this study, it can be analyzed that the immune response cannot be enhanced indefinitely, and there may be a plateau or even a “turning point” after repeated vaccination.
Four doses of inactivated vaccines are difficult to prevent COVID-19 variants
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



