Moderna/Pfizer vaccines: Differences in immune effects mediated by functional antibody Fc.
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Moderna/Pfizer vaccines: Differences in immune effects mediated by functional antibody Fc.
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Moderna/Pfizer vaccines: Differences in immune effects mediated by functional antibody Fc.
In response to the COVID-19 sweeping the world, two mRNA vaccines, BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 , successfully reduced the infection rate and mortality rate of the vaccinated population against the original strain of the new coronavirus at an unprecedented rate of development and production.
With the emergence of COVID-19 mutants that can escape the action of neutralizing antibodies, the efficiency of mRNA vaccines to block infection has decreased, and the number of global breakthrough infections has risen sharply.
However, it is gratifying that, in addition to the elderly group, among these infected people who received the mRNA vaccine, the severe rate, hospitalization rate and mortality rate remained at a very low level , which prompted us to think about the vaccine-triggered immune correlates .
Immune effects mediated by functional antibody Fc
Numerous preliminary immune correlation data suggest a strong correlation between neutralizing antibody titers and vaccine efficacy .
However, for a variety of vaccines, antibody binding titers provide a more robust indication of the protective efficacy of vaccine immunity , since vaccine-triggered protection can be observed before the evolution of neutralizing antibodies.
This protective efficacy persisted even in the presence of weakened neutralizing antibodies. This information prompted us to consider whether there are additional mechanisms of antibody protection in addition to neutralizing antibodies.
In addition to binding and neutralizing antigens, antibodies can utilize Fc receptors and the complement system to mediate a range of additional immune functions .
The immune effect mediated by Fc receptors plays a key role in the preventive treatment of Sipke protein-specific monoclonal antibodies. More importantly, this immune effect can reduce the severity of the disease, not just block the disease . effect of infection.
Although there are currently many data showing that adenovirus vaccines can trigger strong Fc receptor-mediated immune effects, little is known about whether mRNA vaccines can trigger such mechanisms.
Immunity differences triggered by two mRNA vaccines emerge
In the Phase 3 clinical data, BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines both showed strong protection efficiency in preventing infection with the original COVID-19 strain D614G, reaching 94.1% and 95% , respectively .
Although the two mRNA vaccines elicited similar antibody and neutralizing antibody titers, emerging real-world immunology data are beginning to point to differences in immune responses between the two vaccines .
In particular, BNT162b2 had a protection efficiency of 40% in the face of the Delta variant , while mRNA-1273 had a protection efficiency of up to 70% .
There were also differences in the humoral immunity triggered by pregnant women who received the two vaccines, and these differences were suspected to be caused by differences in the dose of vaccination, the encapsulation material, and the interval between vaccinations.
But whether similar differences exist in the non-pregnant population, especially in the face of various variants, remains unknown.
On March 29, 2022 , Galit Alter et al published an article in Science Translational Medicine mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccines elicit antibodies with differences in Fc-mediated effector functions , and found that both vaccines can trigger strong humoral responses,
However, there are significant differences in serum functional antibody-mediated immune effects and epitope recognition . Let’s take a look at the very interesting data obtained in this article.
Both vaccines trigger strong humoral responses
Targeting the original strain D614G
Both vaccines are known to trigger very high serum antibody titers and neutralizing antibody titers , but real-world data are starting to show differences in how the two vaccines prevent infection. The researchers therefore wondered whether the two vaccines would trigger similar Fc receptor-mediated immune effects .
They found that, in the face of the original strain D614G , the two vaccines can trigger the same IgG and IgM binding titers, however, mRNA-1273 can trigger the body to produce more IgA , especially targeting S protein, RBD, NTD and S1 IgA.
Moreover, except that mRNA-1273 induced the production of NTD-specific antibodies with higher FcR binding capacity, the antibodies produced by both vaccines had strong and roughly the same binding capacity to FcR .
Similarly, both vaccine-vaccinated populations with peak immunity developed the same degree of ADCD ( antibody dependent complement deposition ) and ADCP ( anti body dependent cellular phagocytosis by monocytes ) responses.
In contrast, the mRNA-1273 vaccinated population displayed stronger ADNP ( neutrophil phagocytosis ) and ADNKA ( antibody dependent natural killer cell activation ).
In general, in the face of the original strain D614G , both vaccines can trigger strong humoral immunity, but compared with the population vaccinated with BNT162b2, the antibodies produced in the population vaccinated with mRNA-1273 have stronger NTD recognition ability, More IgA immunity, specific antibody-mediated immune effects .
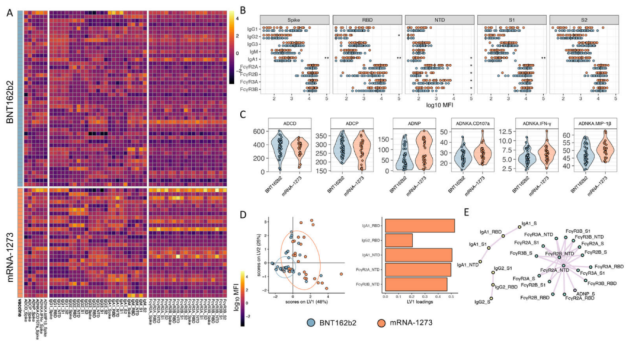
Both vaccines trigger similar antibody effects targeting the original strain
Targeted VOCs mutants
Although the two mRNA vaccines have very significant immune protection against the original strain, with the emergence of various mutant strains, due to various mutations in the amino acids of the Sipke protein, the neutralization induced by the vaccine has been greatly weakened Antibody activity.
Among the various VOCs, the neutralizing activity of the mRNA vaccine-induced antibodies against the Alpha and Gamma mutants was only very weakly reduced, but, for the beta mutants, a very marked reduction was exhibited.
Therefore, researchers want to know what is the difference between the two mRNA-induced serum antibody Fc-mediated immunity in the face of various COVID-19 mutants .
They found that in the face of various new coronavirus mutant strains , both vaccines could trigger an overall similar abundance of functional antibodies targeting the three mutant strains , and their serum antibody Fc-mediated immune responses were also comparable .
However, BNT162b2-triggered antibodies were more IgM- and IgG-biased , while mRNA-1273-triggered antibodies were more IgA- and IgG-biased .
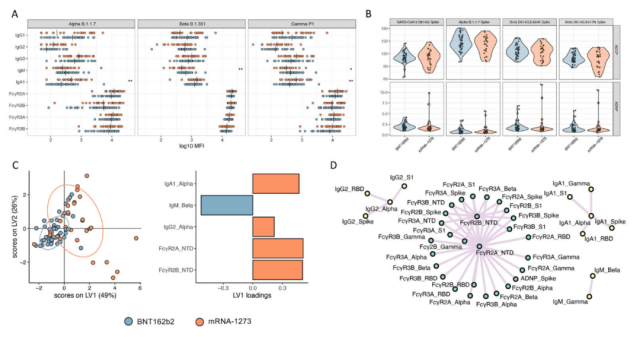 Both vaccines trigger the same degree of serum antibody effect targeting VOCs
Both vaccines trigger the same degree of serum antibody effect targeting VOCs
Differences in serum antibody effects between recovered patients and mRNA vaccine recipients
Studies have shown that the immune line of defense triggered by initial infection or vaccination can be broken through by VOCs mutant strains, resulting in a resurgence of the epidemic.
The researchers compared the immune efficacy mediated by the VOCs mutant RBD-targeting VOCs mutant RBD and the antibody Fc targeting the full-length Spike protein in the serum of recovered patients and mRNA vaccine recipients.
The titers of IgG1 and IgG3 in serum were higher, and the binding ability of these antibodies to VOC RBDs was weaker than that of the original strain D614G RBD.
All RBD-specific antibodies in the sera of mRNA vaccinees also showed a similar trend in their FcR-binding responses, that is, compared with the sera of patients who had recovered from COVID-19, the RBD-specific antibodies in the sera of vaccinees had stronger binding ability to FcR powerful.
In addition, RBD-specific antibody titers were slightly higher in sera from mRNA-1273 vaccinees than in sera from BNT162b2 vaccinees.
In contrast, Spike-specific IgG1 and IgG3 have high binding capacity to full-length Spike from various mutant strains. More importantly, the Spike-specific antibody titers in the sera of the COVID-19 recovered patients were significantly lower than those of the vaccinated sera.
Although the ability of various VOC RBDs antibodies to bind to FcRs has more variability, Spike-specific antibodies have more stable FcR binding abilities .
Considering that the vaccinated population has lasting protection against Delta mutants, but the probability of infection breakthrough increases greatly over time, these data suggest that non-RBD-specific antibodies may be the key to lasting vaccine protection.
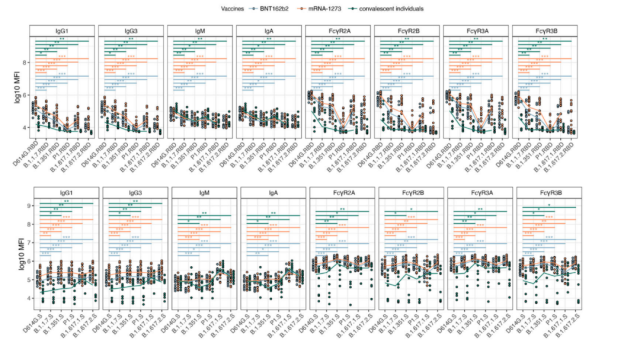 mRNA vaccine can trigger Spike protein-specific antibodies with stronger binding to FcR
mRNA vaccine can trigger Spike protein-specific antibodies with stronger binding to FcR
Depletion of RBD-specific antibodies affects serum antibody-mediated immune effects
The above data suggest that RBD-specific antibodies and Sipke-specific antibodies play different roles in the Fc-mediated immune effects of serovar polyclonal antibodies. Therefore, it is necessary to remove RBD-specific antibodies in serum, and then use various VOC Sipke antigens to measure the immune effect mediated by serum antibodies.
Specifically, despite the presence of many RBD-targeting neutralizing antibodies in sera, the removal of RBD-specific antibodies did not contribute significantly to the immune effect mediated by functional antibody Fc in the sera of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccinees. influence .
Removal of RBD-specific antibodies affected serum ADCP activity in BNT162b2 recipients, but not other immune effects mediated by serum antibody Fc.
Removal of RBD-specific antibodies had very little effect on the immune effect of serum antibodies in mRNA-1273 vaccinees .
In contrast , the immune effect of serum antibodies in recovered patients was significantly affected by the removal of RBD-specific antibodies.
These data suggest that various RBD-specific antibodies play different functions in serum polyclonal antibody-mediated immune efficacy against 2019-nCoV, which may help explain the different immune responses triggered by mutant strains of VOCs with RBD mutations reaction.
Taken together, these data suggest that the two vaccines can strongly trigger different functional serum antibody-mediated immune effects .
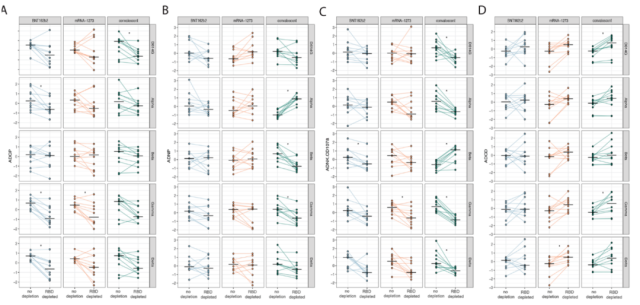
Removal of RBD-specific antibodies affects serum antibody-mediated immune effects in recovered patients
Summary
mRNA vaccines and viral infections can trigger different RBD -centered immune effects in the body. Compared with the immune responses triggered by infected viruses, mRNA vaccines can trigger stronger immune protection effects targeting various new coronavirus mutants.
Interestingly, depletion of RBD-specific antibodies in the serum of recovered patients enhanced ADCD immune effects, suggesting that the presence of specific antibody subsets in serum may block Fc-mediated immune effects, either by blocking other functional sera in serum.
Antibodies come into contact with antigenic epitopes, either by changes in the Fc domain of the antibody following vaccination or infection with a virus.
Considering that neutralizing antibodies are dependent on RBD recognition, the data presented in this article suggest that even if serum RBD-specific antibody levels begin to decline, mRNA vaccines will continue to trigger strong immune effects mediated by functional antibody Fc in serum.
This is used to counteract various VOCs mutants that are resistant to RBD neutralizing antibodies , such as Omicron.
Although these mRNA-triggered non-neutralizing antibodies cannot block virus transmission, they can still confer powerful protection by clearing the virus.
Overall, BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273, both vaccines can trigger strong humoral immunity , but there are differences in epitope recognition and serum antibody-mediated immune effects.
Higher levels of RBD- and NTD-specific IgA were observed in sera of mRNA1273 vaccinators compared with BNT162b2 vaccine , and antibody-mediated phagocytic effects and natural killer cell activation effects were also higher in sera.
Moreover , after removing the specific RBD antibodies in the serum, the differences between the non-RBD-specific antibody-mediated immune effects triggered by the two mRNA vaccines are highlighted , which helps us understand the immune protection conferred by the two mRNA vaccines.
Potential differential mechanisms of potency, providing new clues for the design of vaccines and mAbs that provide long-term protection.
In addition, it should be noted that it is not very clear whether the difference in the immune response induced by the two vaccines is driven by the dose of the vaccine, the interval between two injections, and the LNP composition.
Moderna/Pfizer vaccines: Differences in immune effects mediated by functional antibody Fc.
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



