Arrhythmia burden of indolent lymphoma: atrial fibrillation is the most common
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
- Why Botulinum Toxin Reigns as One of the Deadliest Poisons?
- FDA Approves Pfizer’s One-Time Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B: $3.5 Million per Dose
- Aspirin: Study Finds Greater Benefits for These Colorectal Cancer Patients
- Cancer Can Occur Without Genetic Mutations?
Arrhythmia burden of indolent lymphoma: atrial fibrillation is the most common
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- What is the difference between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Arrhythmia burden of indolent lymphoma: atrial fibrillation is the most common. The results of the study indicate that the risk of arrhythmia in patients with indolent NHL may increase due to treatment.
Research Background
Indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) is composed of a variety of diseases, including marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL), small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SLL/CLL) and Follicular lymphoma (FL).
Because of the long-term natural history of these diseases, the survival rate of patients over several years is often used as a measure. The incidence of arrhythmia in patients with indolent lymphoma is unclear, but recent observations indicate that the problem of arrhythmia is getting worse.
Due to advances in the treatment of indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) and the emergence of new therapies, coupled with the aging of the population and the long natural history of the disease, understanding the arrhythmia burden of indolent lymphoma is important for patients with active treatment of lymphoma. It is important for long-term survivors.
Research method
Indolent NHL adults aged 18 years and older who were treated at the Wilmot Cancer Institute at the University of Rochester between 2013 and 2019 were included in the Oncology Cardiology Lymphatic System Malignancy Database and analyzed.
The main purpose of this study is to determine the incidence of arrhythmic events and sudden cardiac death in patients with indolent lymphoma during treatment. According to the ICD-10 code, arrhythmias include ventricular arrhythmias (VT/VF), atrial arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, and atrial tachycardia), and bradycardia.
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to evaluate the cumulative probability of arrhythmia.
Research results:
A total of 918 patients were diagnosed as indolent NHL. Diagnosis included: 414 cases of CLL, 284 cases of FL, 144 cases of MZL, and 76 cases of LPL. The median age is 64 years old, and 43% of them are women. 383 patients (42%) received treatment.
Treatment is divided into chemotherapy, targeted therapy, monoclonal antibody/immunotherapy and combination therapy. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between patients receiving treatment and those who had never received treatment.
At the time of diagnosis, 277 patients (30%) had a history of hypertension, and 101 patients (11%) had a history of arrhythmia. During a median follow-up of 24 months, 168 patients (18%) developed arrhythmia, of which 63 were patients with a history of arrhythmia and 105 patients were without a history of arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of arrhythmia, with a total of 81 cases (9%).
At 6 months after diagnosis, the cumulative probability of an arrhythmia is 8% (Figure 1).
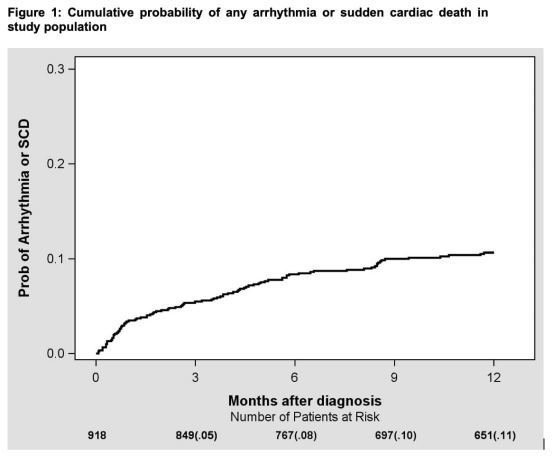
Among all arrhythmias, 89/168 occurred in the SLL/CLL group, 35/168 occurred in the FL group, 17/168 occurred in the LPL group, and 27/168 occurred in the MZL group.
The incidence of arrhythmia in patients receiving chemotherapy alone was 4/95, the incidence of arrhythmia in patients receiving monoclonal antibody/immunotherapy was 12/95, and the incidence of arrhythmia in patients receiving targeted therapy was 28/95.
Most arrhythmias (51/95; 53.6%) occurred in patients receiving combination therapy (chemoimmunotherapy or targeted/immunotherapy).
Overall, 80 patients (9%) died, 10 deaths were related to cardiovascular disease, of which 8/10 (80%) were sudden cardiac death.
Analysis conclusion
The results of the study indicate that the risk of arrhythmia in patients with indolent NHL may increase due to treatment.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia found in this study, and appears to have increased compared with the incidence in the general age-matched population (1-1.8 cases per 100 people per year).
Of the 80 deaths, 8 (10%) were attributed to sudden cardiac death. This data provides important information that can help identify patients with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Prospective monitoring of these patients may better determine the incidence and related risks of arrhythmias.
Future research will focus on the risk factors of arrhythmia, and develop a method to prevent and treat arrhythmia in the indolent NHL patient population.
Arrhythmia burden of indolent lymphoma: atrial fibrillation is the most common
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org



