“Self-death” of coronavirus still needs observing although cases drop sharply in Japan
- Why Lecanemab’s Adoption Faces an Uphill Battle in US?
- Yogurt and High LDL Cholesterol: Can You Still Enjoy It?
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
“Self-death” of coronavirus still needs observing although cases drop sharply in Japan
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
“Self-death” of coronavirus still needs observing although cases drop sharply in Japan.
This Japanese study may be a solitary evidence, and other studies are needed to circumstantial evidence or multiple proofs to confirm that the mutation of the new coronavirus also has negative options.
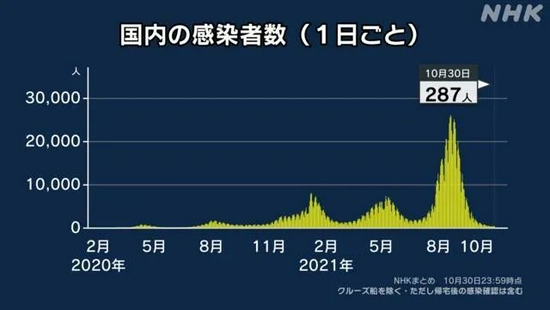
Changes in new cases in Japan. Picture/NHK
According to a recent report by the Kyodo News of Japan, after reaching its peak in August this year, the number of cases in Japan began to plummet. Entering October, the number of newly diagnosed cases in Japan has dropped sharply.
- On October 15, the number of new cases in Japan was only 151, a record low.
- On October 31, there were only 229 new cases in Japan. Even in Tokyo, the “severe disaster area”, there were only 22 new cases. .
Compared with the 25,800 new cases in Japan on August 20 this year, Japan’s recent epidemic has slowed down significantly.
Recently, Japan’s fierce fifth wave of epidemics has seen a steep drop in the number of cases. Although some analyses claim that the epidemic has eased because of the increase in vaccination rates and the reduction of people going out, the speed of vaccination has obviously not reached the speed of alleviation of the epidemic.
The team from Japan’s National Institute of Genetics and Niigata University recently showed that an enzyme in the Delta variant has mutated, resulting in reduced virus activity or inability to spread, that is, a “self-detonation” phenomenon has occurred.

The enzyme called nsp14 is used to replicate the genome when the virus reproduces, but if errors and mutations occur in the process, and errors accumulate, the virus will become unable to reproduce.
Researchers said the situation in Japan is that almost all new coronaviruses have been replaced with nsp14 variants, which means that most of the viruses have died. All newly confirmed diagnoses have also been infected with this “explosive” virus.
The two sides of virus mutation results
The improvement of the epidemic situation in Japan is theoretically due to two main factors, one is the appropriate epidemic prevention policy, and the other is the effective clinical prevention and treatment. However, Japanese researchers believe that the main cause of virus mutation is that it is beneficial to humans but unfavorable to the virus. Moreover, this is a conclusion based on research, not speculation or analysis.
The research team of Japan’s National Institute of Genetics and Niigata University recently published a study showing that an enzyme called nsp14 has been mutated in the genome of the most toxic and faster-spreading delta mutant strain that plagues countries around the world. The virus cannot be repaired in time, making the virus self-extinct. Obviously, this is one of the results of virus mutation.
In May of this year, during the severe epidemic in Japan, there were many cases of under-reporting and under-reporting.
From the perspective of biological evolution theory, there has been a dispute between the terms “evolution” and “evolution” for a long time. The reason why some people prefer to call evolution rather than evolution is that evolution has semantically preconceived that the evolution of organisms only develops in the direction that is beneficial to organisms.
However, in fact, the changes of all living things, including humans, can only be summarized by evolution, because evolution is random, and it can develop in a direction that is beneficial to the organism itself, or it can develop in a direction that is not conducive to the organism itself, such as The extinction of the dinosaurs, the extinction of the Neanderthals.
The same is true for virus mutation. There are at least two results of mutation, one is positive choice, the other is negative choice. The former is good for the virus itself, and the latter is bad for the virus itself.
People have also seen the beneficial results of the virus. Its toxicity has increased and its spread speed has increased. For example, the Delta mutant strain has caused multiple rounds of epidemics.
However, this is only one side of the problem. Even among the most toxic and fastest-spreading Delta mutants, there are more subspecies. Studies to date have shown that there are more than 40 subspecies of Delta.
In the United Kingdom and some parts of the world, there has also been a faster-spreading subspecies of Delta virus AY.4.2, and its transmission rate has increased by about 10% compared with Delta (B.1.617.2).
Moreover, even the subspecies change of the delta mutant strain is not just developing in the direction that is beneficial to the virus, but has another result, that is, negative selection.
This choice is not good for the virus and good for its host-humans. The current research results in Japan have shown this point, which not only proves the duality or diversification of biological evolution, but also presents new situations that are beneficial to mankind that need to be paid attention to in the fight against the epidemic.
The evolutionary path that needs further confirmation
From a scientific point of view, the negative selection of the virus mutation discovered this time is a problem with the repair of the virus genome. A recent study by British researchers believes that the new coronavirus is one of the fastest mutating viruses, mutating almost once a week, and the rate of mutation is more than 50% higher than previously estimated.
The genetic and genomic mutations of all organisms, including humans, will initiate a basic function of organisms, the repair of genetic material (DNA and RNA) to correct the mutated genes. The new coronavirus repairs its mutated RNA genes with the help of the enzyme nsp14, but if the enzyme nsp14 that repairs the mutated genes also mutates, the repair will be delayed or impossible to repair.
In this way, the accumulation of too many mutant genes may cause the virus to fail to reproduce, and thus the virus’s ability to invade human cells is reduced, or it perishes and can no longer harm the human body.
Of course, this Japanese study may be solitary evidence, and other studies are needed to circumstantial evidence or multiple proofs to confirm that the mutation of the new coronavirus also has negative options.
However, at the scientific level, there is already circumstantial evidence. Japanese researchers speculated that the interaction between the enzyme and the enzyme caused the mutation of the nsp14 enzyme, and one of the enzymes called APOBEC changed the nsp14 enzyme. In East Asia and Oceania, there are many people who are particularly active in this enzyme.
At the same time, combined with the changes in the epidemic situation in Japan, it is also consistent with the variation of the nsp14 enzyme. In the fifth wave of the epidemic in Japan, from the peak of the number of cases to the time when it subsided, the infection caused by the nsp14 enzyme mutant virus accounted for almost all the infected cases.
The third wave of the epidemic in Japan from last fall to March this year also has this feature, indicating that the mutation of the new coronavirus does have negative choices and is heading for another evolutionary path of extinction or reduced toxicity and infectivity.
Of course, this research in Japan needs to be confirmed by the results of epidemic research in other countries, but at least the research in Japan and the trend of the epidemic are in line with the evolutionary theory, and it is also supported by preliminary scientific evidence, which deserves further attention.
“Self-death” of coronavirus needs observing although cases drop sharply in Japan
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



