Nature Biomedical Engineering: Nebulized Inhalation of mRNA Vaccine
- Gut Bacteria Enzymes Offer Hope for ABO Universal Blood Transfusions
- Well-Known Japanese Medicine Exposed for 30 Years of Data Falsification
- Oregon Reverses Course: From Decriminalization to Recriminalization of Drug Possession
- Why Lecanemab’s Adoption Faces an Uphill Battle in US?
- Yogurt and High LDL Cholesterol: Can You Still Enjoy It?
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
Nature Biomedical Engineering: Nebulized Inhalation of mRNA Vaccine
- Was COVID virus leaked from the Chinese WIV lab?
- HIV Cure Research: New Study Links Viral DNA Levels to Spontaneous Control
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Nature Biomedical Engineering: Nebulized Inhalation of mRNA Vaccine
Nature Reviews Materials published a Research Highlights: Nebulized lipid nanoparticles on October 18, 2021.
Quoting from Philip J. Santangelo (Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University School of Medicine): “Different from traditional systemic delivery of mRNA vaccines, the primary problem of aerosolized mRNA vaccines is the stability of the mRNA vaccine under the action of aerosolized shear force. , as well as epithelial cells is efficiently absorbed , and do not induce inflammation .The mRNA-nanoparticle formulation first has to survive the nebulizer, that is, shear forces that can disrupt its structure, and then has to be taken up efficiently by the epithelium without inducing inflammation”
This article by Highlights was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering in September 2021: “Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nebulized therapeutic mRNA to the lungs”. Authors from the Georgia Institute of Technology , Emory University School of Medicine .

Research methods
Researchers have developed an in vivo cluster-based iterative screening approach (in vivo cluster-based iterative screening approach).
The workflow is based on the definition of different chemical features, each of which acts as an axis in the N-dimensional chemical space.
The characteristics include the amount of polyethylene glycol (PEG) added to the lipid nanoparticles , the lipid-polyethylene glycol molecular structure , the charge of the phospholipids , and the presence or absence of cholesterol .
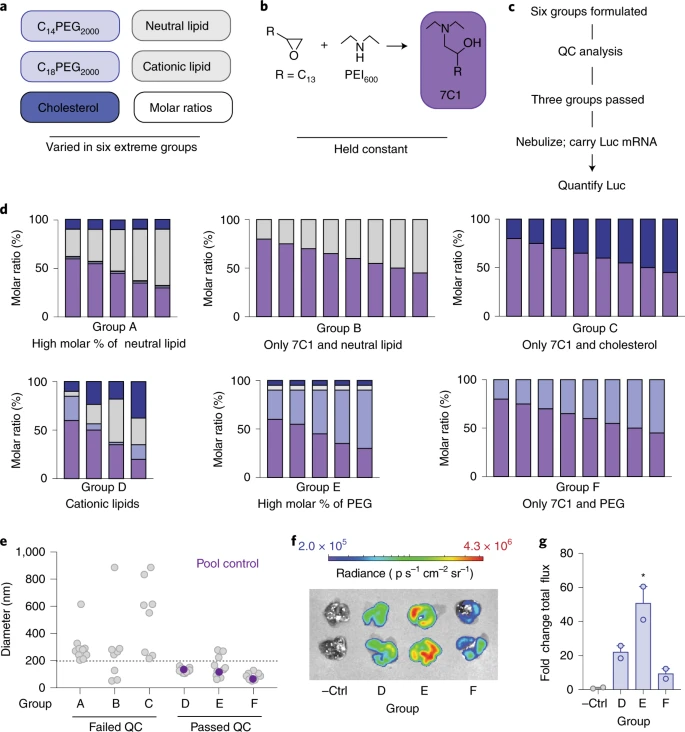
In this design, based on the oligomeric lipid co-linked compound 7C1, 6 extreme groups are defined by different molar ratios , components and charges , each with 8-12 lipid nanoparticles.
Research result
These nanoparticles can pass through the nebulization reaction in the body while detecting the delivery efficiency of mRNA.
Using this workflow, the authors discovered that PEG-lipid molecules, rather than cholesterol and auxiliary lipids, are essential for the formation of stable 7c1-based lipid nanoparticles.
In addition, the combination of cationic auxiliary lipids and high mole percentages increased mRNA delivery after nebulization , indicating that the chemical characteristics of nanoparticles play a more important role in nebulization delivery than particle size .
Based on these design rules, a new type of nanoparticles containing high PEG lipids and cationic auxiliary lipids was designed for lung delivery, called nebulized lung delivery 1 (NLD1) .
NLD1 can effectively deliver mRNA encoding the therapeutic antibody FI6, which binds to hemagglutinin to neutralize various subtypes of influenza virus.
Pretreatment with NLD1 by nebulization method saved the lives of mice vaccinated with influenza virus H1N1.
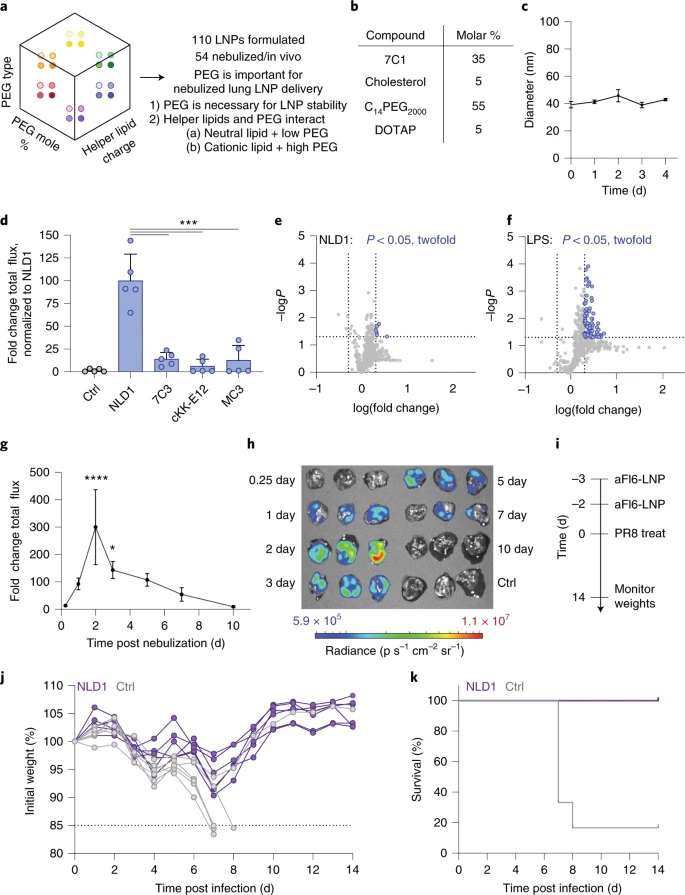
Another corresponding author of the article, James E. Dahlman, commented: “Using these direct in vivo screenings, we have discovered that NLD2, a second-generation aerosolized lipid nanoparticle, is superior to NLD1 in terms of delivery efficiency.
Using these direct in vivo screens, we have already found NLD2, a second-generation nebulized lipid nanoparticle, which outperforms NLD1in terms of delivery efficiency”
Summary
The continuous mutation of SARS-CoV-2 puts forward higher requirements for continuous prevention and control.
Traditional mRNA vaccines are injected intramuscularly, which puts forward higher requirements for dosage form stability, storage, transportation, side-effect monitoring, etc.
It also limits the availability of vaccines in underdeveloped areas, which is a dead end for disease prevention and control.
Aerosol inhalation of mRNA vaccines, in comparison, will increase the convenience of vaccine use, act on the upper respiratory tract, reduce the incidence of systemic adverse reactions, increase the vaccination rate in underdeveloped areas, and help eliminate the new coronavirus globally.
However, aerosol inhalation also has its own unique technical requirements, such as stability under the action of aerosol shearing force, and the effectiveness of mRNA delivery.
Scientists from Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University invented the LNP formula for lung-specific delivery of mRNA vaccines: high PEG lipids and cationic auxiliary lipids , laying the foundation for the development of aerosolized mRNA vaccines.
Reference:
Melissa P. Lokugamage et al, Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nebulized therapeutic mRNA to the lungs, Nat Biomed Eng. 2021 Sep;5(9):1059-1068.
Christine Horejs, Nebulized lipid nanoparticles, Nat Rev Mater. 2021 Oct 18; 1. doi: 10.1038/s41578-021-00392-y.
Eygeris Y, Gupta M, Kim J, Sahay G. Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Dec 1. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00544.
Nature Biomedical Engineering: Nebulized Inhalation of mRNA Vaccine
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



