Nature: Cancer gene mutation frequencies for the U.S. population
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Nature: Cancer gene mutation frequencies for the U.S. population
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Nature: Cancer gene mutation frequencies for the U.S. population.
Cancer is usually caused by gene mutations caused by various reasons, but which genes are most frequently mutated in cancer?
You may not expect that this genetic problem is still unanswered in the rapid development of cancer genomics.
Recently, researchers from the University of Virginia and the Salk Institute published a paper entitled “Cancer gene mutation frequencies for the U.S. population” in the journal Nature Commnications.
This paper answers a very basic question: What are the most common mutated genes in human cancers?
The research team combined gene mutation information with cancer prevalence data, revealing the genetic basis of cancer in the entire U.S. cancer patient population.
This work reveals how often each gene is mutated in cancer patients, and these findings can help guide the development of more effective cancer treatments.

Gene mutations play a vital role in the occurrence and development of cancer, and these mutated genes can also be effective therapeutic targets.
Although many studies have identified the genetic mutations involved in certain cancers, there is no research system to reveal which genetic mutations are most common in the entire cancer patient population.
In this new study, the research team combined genomics and epidemiological cancer research data sets to determine what percentage of all cancer patients will have which genetic mutations.
At first, the research team thought that this work seemed simple, but soon after they started, they discovered the problem: genomics and epidemiological research did not use a universal nomenclature system for various cancers.
For example, some researchers classify cancers based on body parts, while others classify cancers based on tumor type, and many researchers use the two together. This makes data organization difficult.
In order to overcome this challenge, the research team carefully analyzed more than 200 studies and individually reviewed and reclassified each cancer according to the universal naming system, and then performed data comparison and statistical analysis.
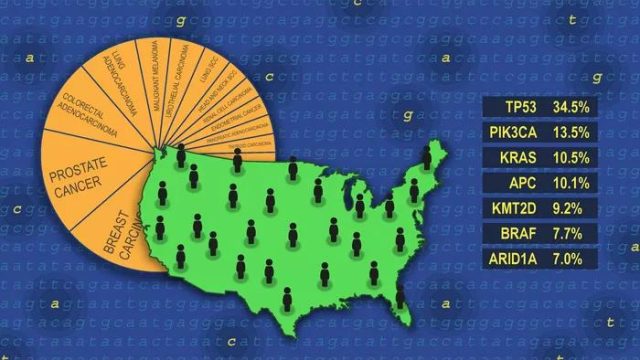
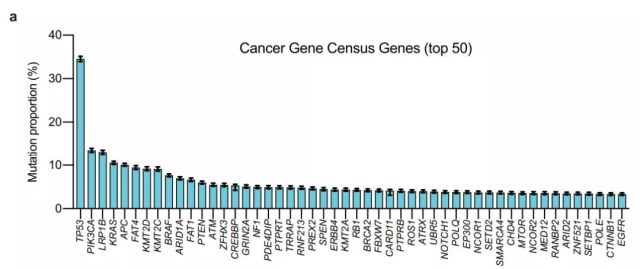
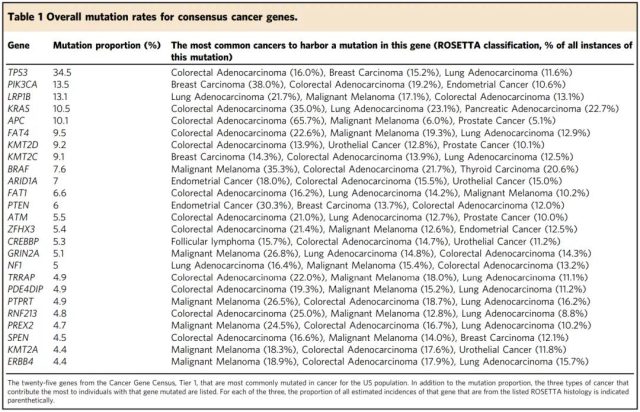
The research team found that the most common gene mutation in cancer is TP53 (34.5%), followed by PIK3CA (13.5%), and LRP1B (13.1%). Surprisingly, only 11% of cancers have KRAS mutations. This is far below the 25% previously thought. Also in the top ten are APC, FAT4, KMT2D, KMT2C, and BRAF.
The most common mutation gene TOP 50 in cancer
Specific data on TOP25, the most common mutation gene in cancer
This is the first time that the frequency and proportion of gene mutations have been evaluated in all cancers. These results suggest that we need to reassess which areas we should focus time, energy and resources on. These findings can help guide the development of more effective cancer treatments.
Paper link:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26213-y
Top 50 of the most common mutant genes in human cancers
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



