Alzheimer disease: Acidify the intracellular environment to remove amyloid
- Normal Liver Cells Found to Promote Cancer Metastasis to the Liver
- Nearly 80% Complete Remission: Breakthrough in ADC Anti-Tumor Treatment
- Vaccination Against Common Diseases May Prevent Dementia!
- New Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Diagnosis and Staging Criteria
- Breakthrough in Alzheimer’s Disease: New Nasal Spray Halts Cognitive Decline by Targeting Toxic Protein
- Can the Tap Water at the Paris Olympics be Drunk Directly?
Alzheimer disease: Acidify the intracellular environment to remove amyloid
- Should China be held legally responsible for the US’s $18 trillion COVID losses?
- CT Radiation Exposure Linked to Blood Cancer in Children and Adolescents
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Alzheimer disease: Acidify the intracellular environment to remove amyloid
Alzheimer’s disease can be cured? eLife: Acidify the intracellular environment to remove amyloid.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), commonly known as “Alzheimer’s disease”, has about 50 million cases of dementia worldwide, with about 10 million new cases every year. In China, there are tens of millions of patients, ranking first in the world.
21741635809616800
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), commonly known as “Alzheimer’s disease”, has about 50 million cases of dementia worldwide, with about 10 million new cases every year. Although the scientific community has invested a lot of energy in Alzheimer’s disease, there is still no very effective treatment plan to prevent or cure Alzheimer’s disease.
Recently, researchers from University of Texas published a research paper entitled “NHE6 depletion corrects ApoE4-mediated synaptic impairments and reduces amyloid plaque load” in the ” eLife ” journal
The study showed that when genetic technology is used to turn off the NHE6 gene, the pH in brain cells will be acidified, which can eliminate the formation of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models and prevent the accumulation of amyloid .

Early studies have shown that the most important genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease is apolipoprotein (ApoE4), which is one of three variants of a protein involved in fat metabolism in mammals.
In humans, compared with the most common variant ApoE3, the average age of onset of Alzheimer’s disease with ApoE4 variants has been reduced by several years, and the more rare ApoE2 seems to have a protective effect on this disease.
The three variants are very similar in structure. Compared with ApoE2, ApoE3 contains an amino acid substitution, which causes the protein to have a higher positive charge. The ApoE4 variant contains two amino acid substitutions, and the protein has the highest positive charge.
In this study, the researchers focused on the organelles responsible for protein sorting, recycling, or transporting proteins to the lysosome through the interior of the cell . Earlier studies have shown that the organelles of humans and animals carrying the ApoE4 gene are enlarged compared to humans and animals carrying the other two apolipoprotein variants.
The researchers used genetically modified mice to simulate Alzheimer’s disease and produce human forms of ApoE4 and amyloid beta protein. They found that it is precisely because of the positive charge on ApoE4 that this protein aggregates in the organelles. , The charge of ApoE4 matches the charge of the internal environment of the inner body.
However, this aggregation prevents these organelles from continuing to transport, recirculate, or help process other proteins, including amyloid beta.
When the researchers used genetic technology to turn off a gene called NHE6, they found that the negative effects of ApoE4 were eliminated, and the protein was transported in the cell without obstacles. NHE6 acts as the pH regulator of the endosome, and the protein produced by it exchanges acidic protons into sodium ions.
When the researchers turned off the NHE6 gene, it no longer produces pH-adjusting proteins, and the organelles quickly become more acidic, and this biochemical change prevents the accumulation of amyloid beta .
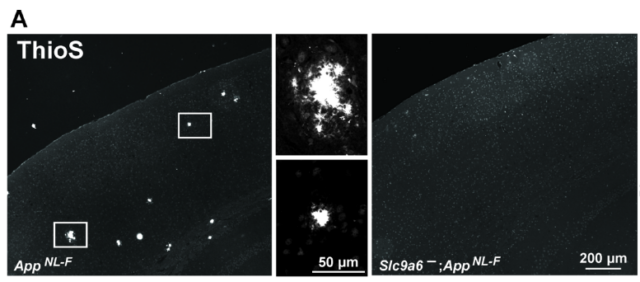
Turning off the NHE6 gene prevents the accumulation of amyloid beta
It is worth noting and unexpectedly that inhibiting the NHE6 gene in mice effectively inhibits amyloid deposition even in the absence of ApoE4 , indicating that the accelerated acidification of organelles caused by the lack of NHE6 prevents amyloid plaques Formation.
Therefore, NHE6 inhibition or inhibition may be a universal, ApoE-independent method to prevent the accumulation of amyloid in the brain. These findings suggest a new treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.
In conclusion, studies have shown that organelle acidification has considerable potential as a new preventive treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, and may also be used to prevent disease progression.
Paper link:
DOI: 10.7554 / eLife.72034
Alzheimer disease: Acidify the intracellular environment to remove amyloid
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



