Study confirms that it’s not beta amyloid that causes Alzheimer’s disease!
- Why Lecanemab’s Adoption Faces an Uphill Battle in US?
- Yogurt and High LDL Cholesterol: Can You Still Enjoy It?
- WHO Releases Global Influenza Vaccine Market Study in 2024
- HIV Infections Linked to Unlicensed Spa’s Vampire Facial Treatments
- A Single US$2.15-Million Injection to Block 90% of Cancer Cell Formation
- WIV: Prevention of New Disease X and Investigation of the Origin of COVID-19
Study confirms that it’s not beta amyloid that causes Alzheimer’s disease!
- Red Yeast Rice Scare Grips Japan: Over 114 Hospitalized and 5 Deaths
- Long COVID Brain Fog: Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Persistent Inflammation
- FDA has mandated a top-level black box warning for all marketed CAR-T therapies
- Can people with high blood pressure eat peanuts?
- What is the difference between dopamine and dobutamine?
- How long can the patient live after heart stent surgery?
Study confirms that it’s not beta amyloid that causes Alzheimer’s disease!
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), commonly known as Alzheimer’s disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that occurs mostly in people over the age of 65.
The deposition of amyloid beta protein outside the nerve cells in the brain (also known as senile plaques) is the main lesion of Alzheimer’s disease, and the theory of amyloid beta protein is also considered to be the mainstream pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Based on this, scientists hope to prevent and treat Alzheimer’s disease by inhibiting the production, fibrosis and deposition of β-amyloid. However, the effect is not satisfactory.
The existing drugs can only delay the aggravation of pathological symptoms, but cannot prevent Or reverse the disease process, and it is easy to relapse after stopping the drug.
Knowing a lot of pathological mechanisms, but still unable to get in, we can’t help thinking: Are we really touching the root cause of Alzheimer’s disease, or are we blinded by its appearance, and ultimately cure the symptoms but not the root cause?
Recently, a new study from the Grossman School of Medicine of New York University and the Nathan Klein Institute has subverted our understanding of Alzheimer’s disease “first the formation of extracellular amyloid plaques, and then the death of nerve cells”.
According to the traditional impression, it is proposed that ” neural cells die first, followed by the appearance of extracellular amyloid plaques “.
Thinking about it this way, even if the extracellular amyloid plaques are removed, the victim cells have already died, so what is the remedy?
The study, titled “Faulty autolysosome acidification in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models induces autophagic build-up of Aβ in neurons, yielding senile plaques”, was published in Nature Neuroscience on June 2.

Researchers believe that Alzheimer’s disease begins with neuronal autophagy-lysosomal dysfunction, or more precisely, “acidification” disorders .
Autophagy lysosomes are formed by the fusion of autophagic vacuoles and lysosomes.
If lysosomes are compared to garbage disposal plants, autophagic vacuoles are equivalent to “garbage trucks”, which transfer damaged proteins, nucleic acids, organelles, etc. Transported to lysosomes for catabolic digestion.
The hydrolase in the lysosome needs to be in an acidic environment to perform digestion and decomposition, and this acidic environment is mainly achieved by the proton pump vATPase to pump the H+ ions in the cytoplasm into the lysosome.
The assembly line of β-amyloid will stagnate, causing a large number of garbage intermediates to form and accumulate in the lysosome, which also includes beta-amyloid and its precursor proteins.
When the lysosome cannot withstand the rupture, the hydrolase in the lysosome is released into the cytoplasm, decomposes and digests the cell, the cell membrane disintegrates, the intracellular garbage is leaked out, and finally the “extracellular” amyloid we see is formed.
In other words, cell death precedes the formation of extracellular amyloid plaques, and it can even be said that these amyloid plaques are the remains of dead nerve cells mixed with beta amyloid .
So how did the researchers justify their conclusions?
First, they needed to observe, in Alzheimer’s mice, that the acidification of nerve cells’ lysosomes is impaired, and that this process precedes cell death and the formation of extracellular amyloid plaques.
Let’s see how they differentiate between normal and acidification-disordered autophagolysosomes:
Autophagic vacuoles (Thy-1 mRFP-eGFP-LC3, TRGL mice) in neural cells were specifically labeled with red-green fluorescent tandem probes, at which time the red and green fluorescence of autophagic vacuoles fused together and emitted yellow Fluorescence.
When the autophagosome is combined with the lysosome, affected by the acidic environment in the lysosome, the yellow fluorescence gradually turns into red fluorescence, coupled with the blue fluorescent marker (CTSD) of the lysosome , the autophagy is finally formed. Lysosomes show purple fluorescence, which is an autophagic lysosome with normal acidification function.
If the acidification function of lysosome is impaired, the yellow fluorescence of autophagosome does not change to red after fusion, and the blue fluorescent mark of lysosome is added, and the finally formed autophagolysosome exhibits white fluorescence, which is acidification dysfunction. of autophagy lysosomes.
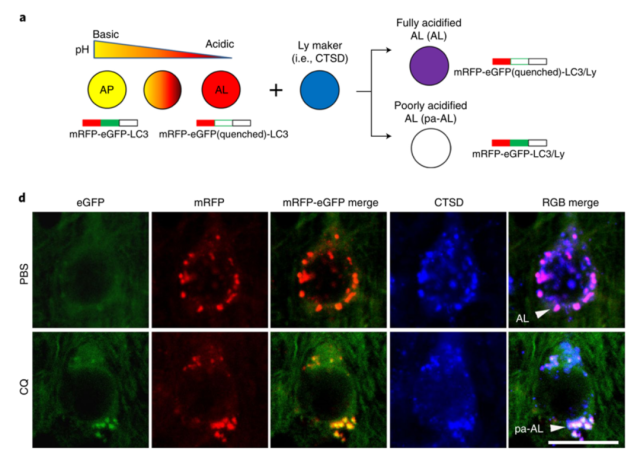
When this probe was applied to model mice of Alzheimer’s disease, the researchers observed that 90% of autophagy-lysosomes in the neocortical region of the mice had acidification disturbances at 5 months after birth.
They appear at least 5 months earlier in the appearance of amyloid plaques in the brain (10-12 months) .
In the early-onset Alzheimer’s disease model 5xFAD mice, the autophagy-lysosomal acidification disorder appeared earlier, and the acidification-impaired autophagy-lysosomes can be found in the brains of 2-month-old 5xFAD mice and neuronal degeneration.
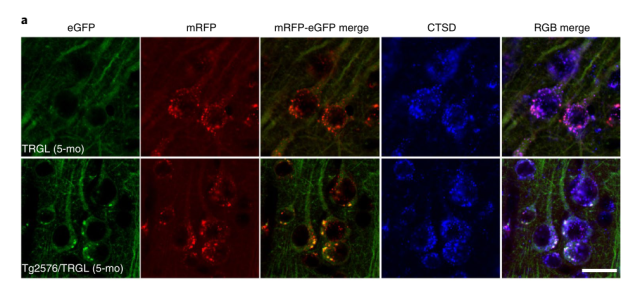
Correspondingly, the proton pump vATPase activity on the lysosomes of these Tg2567 mice was significantly decreased (65.6 ± 4.1%) in the lysosomes of their nerve cells at 6 months after birth compared with wild-type mice of the same age (65.6 ± 4.1%) . Monthly, it was even less than half (45.3 ± 3.7%) .
Acidification-impaired autophagolysosomes cannot digest damaged proteins, resulting in the accumulation of junk intermediates, products of beta amyloid precursor protein (APP-βCTF) and beta amyloid, in autophagolysosomes.
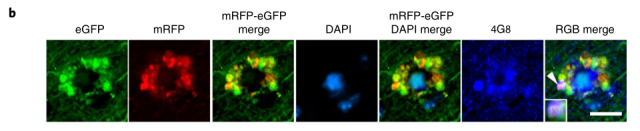
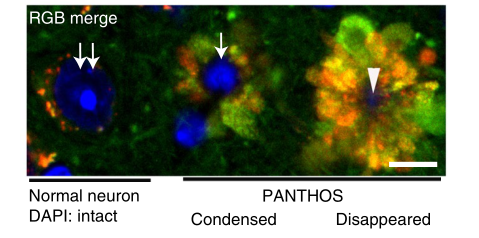
Not only that, these autophagolysosomes are like petals, fused with each other around the nucleus to form a corolla-like structure, which the researchers call PANTHOS (poisonous flower) , and the nerve cells containing poisonous flowers in the body are also called “” Poison Flower Neurons”.
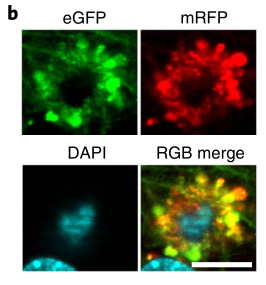
As the disease progresses, in addition to the increase in intracellular beta amyloid, the “poisonous flower neurons” gradually develop towards senile plaques.
If only half of the “poisonous flower neurons” have senile plaques in the brains of 2.2-month-old 5xFAD mice.
Marker-positive, the proportion has exceeded 95% in 6-month-old 5xFAD mice.
Eventually, the nucleus in the center of the poisonous flower disappears, the permeability of the lysosome increases, the enzymes in the lysosome are released into the cytoplasm, the integrity of the nerve cell membrane disappears, the cell is declared dead, and the remains become what we see as “extracellular plaques” , more and more “poison flower neurons” gathered together, and the plaque area further increased.
For the hesitant Alzheimer’s disease treatment, this research is tantamount to “pulling through the clouds and seeing the sun”.
The cause of Alzheimer’s disease is not outside the cell, but inside the cell.
To reduce plaque formation and avoid cell death, the key is to “repair the garbage disposal plant” and restore the acidification function of lysosomes.
In fact, the team’s research published in Science Advances in April this year has demonstrated that by improving lysosomal acidification, it can significantly reduce neural damage in Alzheimer’s mice!
Hopefully this time we are truly on a path to truth and hope.
References:
[1]Lee JH, Yang DS, Goulbourne CN, et al. Faulty autolysosome acidification in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models induces autophagic build-up of Aβ in neurons, yielding senile plaques [published online ahead of print, 2022 Jun 2]. Nat Neurosci. 2022;10.1038/s41593-022-01084-8. doi:10.1038/s41593-022-01084-8
[2]Lie PPY, Yoo L, Goulbourne CN, et al. Axonal transport of late endosomes and amphisomes is selectively modulated by local Ca2+ efflux and disrupted by PSEN1 loss of function. Sci Adv. 2022;8(17):eabj5716. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abj5716
Study confirms that it’s not beta amyloid that causes Alzheimer’s disease!
(source:internet, reference only)
Disclaimer of medicaltrend.org
Important Note: The information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice.



